Psoriasis
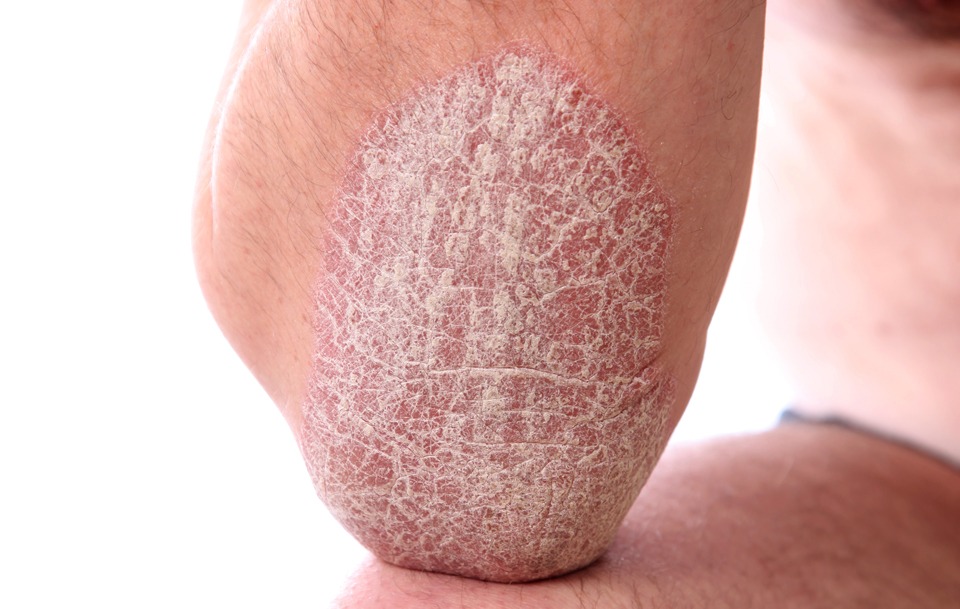
The psoriasis is probably the most common and popular skin disease with a prevalence of 2-3% in the general population. It is presented in a very variable way between patients and usually goes through periods of stability and outbreaks throughout life. Each person has a specific and unique type of psoriasis, either for the location and type of injury or for the interaction between the disease and the person, since the degree of impact it has on each person is different. However, the most typical form, called “in plaques”, shows very rich semiological features that allow, in most cases, a fast and accurate diagnosis.
It is a chronic condition of the skin that despite not being a serious pathology, if it has a very important implication in the quality of life of the person. Mostly, it is characterized by the appearance of erythematous and hyperkeratotic plaques (with redness and crusting) on the elbows, knees and scalp. Although it usually affects the skin exclusively, there is a certain incidence of nail injuries and inflammation in the joints (psoriatic arthritis).
Although always considered as an exclusively cutaneous disease, it is now known that the inflammatory phenomena that lead to the appearance of plaques of psoriasis favor the manifestation of other systemic diseases (comorbidity).
It is for this reason that the early diagnosis of psoriasis and the routine monitoring of other diseases coexisting in the patient are considered very important. The presence of this comorbidity often determines the treatment to be prescribed to treat psoriasis and the patient’s overall prognosis.
Although the origin of the condition is unknown, it is known that there are inflammatory processes in the lesions of the skin due to an abnormal immune response. It is for this reason that the treatments, basically have an anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory action.
It is often advisable to use topical preparations and in cases of severe psoriasis, oral drugs are given. However, it should be noted that it is common for psoriasis to affect a large part of the body or to have a chronic course, which contraindicates the use of these drugs because of their adverse effects. For this reason it is especially useful to treat it with phototherapy, which consists of the application of ultraviolet radiation of type A and / or B.
Read more here